Today's medical portable devices make it easy for patients to self-medicate, move around, and even use equipment when they are out. In order to realize the "portable" features of portable electronic medical devices, it is necessary to have the characteristics of miniaturization and low power consumption.
In addition, these devices require extreme precision to ensure patient safety. Medical devices use a variety of different sensors to monitor the health of the patient, and then the sensor converts the physiological signals into electrical signals for analysis by the electronic device. Signal path design is especially important for portable medical devices because the signals transmitted in medical devices are relatively weak and subject to interference from many sources of noise. This article will discuss how to connect sensors to matched PowerWise amplifiers for both ECG and blood glucose meter applications to extend battery life and improve diagnostic safety.
Operating principle of electrocardiograph
The electrocardiograph (ECG) records the patient's heartbeat activity in real time. The heartbeat signal is measured by three electrodes connected to the patient's body. Figure 1 shows the ECG signal output from one of the electrodes. The figure contains five measurement points, Q, P, R, S, and T. These measurement points can be used to diagnose the possibility of a patient suffering from heart disease.
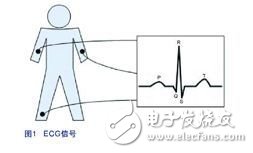
The signal collected from the electrodes is in the range of 400 μV up to 5 mV with a 3 dB corner frequency at 0.05 Hz and 100 Hz. Such signals are generally subject to a lot of interference, such as electrode contact noise, power line noise (50 MHz), breathing, muscle activity, and interference from other electronic devices.
ECG signal adjustment
As stated above, the ECG's signal path must be able to modulate noise from different sources. To combat DC noise, a high-pass filter can be used. However, the most troublesome is the 50Hz noise because it is just in the same range as the frequency we collect. To eliminate this common mode noise, a measurement instrumentation amplifier needs to be built. This configuration is ideal because it amplifies the useful differential signal while rejecting the common-mode voltage, which helps to separate the weakly valid signal from the background noise. As shown in Figure 2, this instrumentation amplifier is implemented with the LMP2234 (four-channel, micropower, high-precision RRO operational amplifier) ​​and high-precision resistors (0.1%).
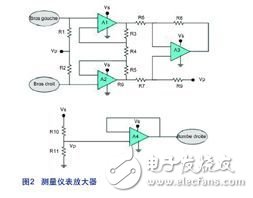
A1, A2, A3, A4: LMP2234
R1, R2: 2 MΩ
R3, R5: 40 kΩ
R4: 20 kΩ
R6, R7: 10 kΩ
R8, R9: 10 kΩ
R10, R11: 20 Kω
The LMP2234 is fabricated using the VIP50 process technology, an insulated silicon BiCMOS process. Ultra-low power amplifiers fabricated in this process are ideal for battery-powered, low-power applications. The process has an operating voltage range of 1.8 to 5.5V and a quiescent current of 36μA to extend battery life in portable systems. The LMP2234 is a member of the LMP family of precision amplifiers, and its high-impedance CMOS input makes it an ideal choice for measurement instruments and other sensor interface applications.
Since the amplitude of the signal from the electrode is extremely low, the DC parameters of the amplifier are important. The LMP2234 has a maximum offset voltage of 150V (typically 10 V), while the offset voltage drift temperature coefficient and bias current are only 0.3 μV/°C and ±20 fA, respectively. These high-precision, tight specifications allow the LMP2334 to perform exceptionally well in maintaining system accuracy and long-term stability.
This measurement instrumentation amplifier contains two stages. The last stage (ie, the output stage) is a differential amplifier that rejects the DC level and both the interference and noise voltage sources that affect both inputs. The first stage (ie, the input stage) consisting of two amplifiers is configured as a buffer that isolates the input. However, based on the mismatch between the amplifiers, they cannot be connected to each other, so a balancing resistor is added between the two amplifiers. Multiplying the gains of the two stages yields the gain of the metering amplifier. In theory, the common mode rejection ratio (CMPR) should be infinite, but due to the resistor mismatch, the non-zero common-mode gain of the output stage is very small. In the input stage of the circuit, the current flowing through all the resistors is the same. This depends on the LMP2234's high input impedance and low input bias current.
The output voltage is defined as:
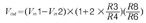
The maximum amplitude of the input signal is only 5mV, but in order to establish the gain, we must consider the DC offset voltage of the electrode, which can sometimes be as high as ±300mV. The rail-to-rail output of the LMP2234 swings from the supply rail to 15mV, increasing the dynamic range of the system. In addition, a bias voltage divider consisting of R10 and R11 provides a voltage that is exactly half the supply voltage required for the patient's sign in the correct patient segment.
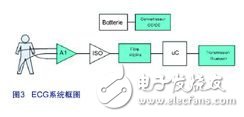
As shown in Figure 3, a high-pass filter is used to suppress DC devices that can cause saturation of the next gain stage. The high pass filter has a cutoff frequency of 0.5 Hz. The filter is implemented using a second-order Sallen Key-type Butterworth topology. The second stage is a low-pass filter with a cutoff frequency of 100 Hz and a gain of 100, and is also implemented in a Sallen Key topology. The analog filters of the Sallen Key class are built around an operational amplifier with resistors and capacitors. The inductor was not used because it was too bulky, bulky, and not perfect.
C1: 1 μF R3: 5.36 kΩ
C2: 220 nF R4: 14.3 kΩ
R1: 1.24 MΩ C3: 33 nF
R2: 365 kΩ C4: 1 μF
R5: 10 kΩ
R6: 1 MΩ
Both filters are implemented using the low-power op amp LMV552, which is fabricated using National's VIP50 process. With a bandwidth of 3MHz, each amplifier consumes only 34μA of current, and the bandwidth/power ratio is the highest in its class of op amps. The LMV552 has a rail-to-rail output stage and an input common-mode range that extends below ground. The operating supply voltage range is 2.7V to 5.5V.
A battery operated system requires a DC/DC boost to provide the 3.3V required for the signal path. The LM2623 is a high efficiency, general purpose step-up DC-DC switching regulator designed for battery-operated low input voltage systems. The regulator accepts input voltages from 8V to 14V and converts them to a stable output voltage of 1.24V to 14V. With the LM2623, the system can be as efficient as 90%.
If the system requires patient safety isolation, it can be achieved by using galvanic isolaTIon, optocoupler capacitance and magnetic coupling. Although this article focuses on the front end of ECG, when developing medical electronic systems, the issue of safety standards cannot be ignored.
Bluetooth transmission
Heartbeat recordings can be wirelessly transmitted to a computer, mobile phone or PDA. Bluetooth technology is stable, reliable, easy to use, cost-effective, and has a wide range of coverage, making it a popular wireless technology for patient monitoring.
National's LMX9838 Bluetooth Serial Port Module is a highly integrated device that includes a Bluetooth 2.0 baseband controller, 2.4GHz radio, crystal, antenna, LDO, and discrete components. The Bluetooth node is fully functional and compact (10 mm x 17 mm x 2.0 mm).
Hardware and software are included in this complete solution for applications with complete high and low Bluetooth stacking layers, Universal Access Gauge (GAP), Service Discovery Application Specification (SDAP) and Serial Port Specification (SPP). The module includes a configurable service database to accommodate additional service specification requirements on the master. In addition, the LMX9838 is certified for Bluetooth end product and can be used directly in the final application without any testing or payment technology license fees.
Based on National's CompactRISC 16-bit processor architecture and digital smart radio technology, the LMX9838 is an optimized solution that fully satisfies the data processing and link management requirements required by Bluetooth nodes.
Coupletech Co., Ltd, could supply CW Laser models for medical instruments and scientific research, Q-Switched Pulse Laser models, NPLP-SEED Laser Head (Laser head), Diode-pumped pulsed Laser and Athermal Diode-pumped Pulsed Laser. e.g. UV laser, Low noise blue laser, Signal mode green laser, Sodium Yellow Laser, Light yellow Laser, Orange yellow laser, Infrared laser, Mid-infrared laser, Eye-safety Laser, Deep UV laser, 900ps-laser head, Diode-pumped Pulsed Laser without temperature control. Coupletech's laser have advantage with small volume, low weight and high reliability.
Coupletech Co., Ltd. has the R&D, Engineering, and Production expertise to manufacture lasers that are able to maintain integrity in various extreme settings and conditions. Coupletech offers diversity of laser sources for a broad range of commercial and scientific applications. We specialize in designing and manufacturing custom-made and OEM lasers to suit our clients' particular needs.

Laser Distance Measuring,Pulse Laser,Laser Diode Specifications,Yellow Laser,CW Laser,Solid-state laser
Coupletech Co., Ltd. , https://www.coupletech.com
