
Bluetooth Low Energy ( BLE ) is one of the most power-efficient short-range wireless communication technologies in the world. Its low power consumption has made it a favorite among both developers and users. With the introduction of the Bluetooth mesh network, many developers are asking: Is the Bluetooth mesh also designed to be energy-efficient? Does it inherit the low power advantages of BLE?
The answer is yes! Bluetooth mesh networks include various optimizations to reduce power usage, especially a feature called "Friendship."
Overview of the Bluetooth Mesh Network Standard
The Friendship feature in a Bluetooth mesh network can be used in various ways. For example, devices like lights are usually connected to a power source, so their power consumption is negligible compared to the light itself. However, other devices such as sensors or smart locks may have limited power, meaning they rely on small batteries or energy harvesting. These types of devices benefit the most from the Friendship concept in Bluetooth mesh networks.
If you’ve read our previous article in this Bluetooth mesh series, you already know that a node is a device that's part of the mesh network. Each node can perform functions related to its product type, as well as support network operations and take on specific roles.
This depends on the features the node supports. All nodes can send and receive messages on the network. In addition, nodes can optionally support one or more additional network features, including:
·       Relay function: The ability to receive and retransmit mesh messages over a broadcast bearer to extend the network coverage.
·       Proxy function: The ability to forward messages between GATT and broadcast bearers.
·       Low Power Node (LPN): A node that reduces its receiver duty cycle significantly to save power. By doing so, the LPN minimizes the time the radio is active, thus reducing overall power use. This is achieved by establishing a friendship with a Friend node.
·       Friendship function: A Friend node stores messages intended for an LPN and forwards them only when the LPN explicitly requests them.
To understand how Friendship helps reduce power consumption, consider a sensor. A good example of a sensor that uses the Friendship feature and acts as an LPN. Such sensors often transmit data infrequently and rarely need to receive messages. For instance, a temperature sensor might only send readings if it detects a change outside predefined limits, which could happen just twice a day. This low transmission frequency keeps power consumption very low.
But what if those temperature thresholds need to be updated based on seasonal changes, and configuration messages must be sent to the sensors? If the sensor needs to receive these messages directly, it would have to stay in listening mode, consuming power even when no messages are being received.
By working with a Friend node, the LPN can schedule its wireless reception at times that make sense for the device, rather than staying constantly active. The LPN polls the Friend node for new messages, and the Friend node only stores messages occasionally. This is how power is saved effectively.
Friend and Low Power Nodes
An LPN must establish a relationship with another node that supports the Friendship function to reduce its receiver duty cycle and save energy. Figure 1 comes from the Bluetooth mesh specification and shows the relationship between LPNs and Friend nodes.
·       Light blue: LPNs
·       Dark grey: Friend nodes associated with specific LPNs
·       Light grey: Friend nodes not associated with any LPN
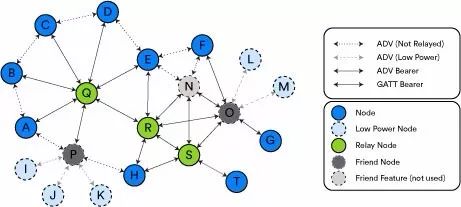
Figure 1 - Example of a mesh network topology
Friend node P has a Friendship relationship with LPN I, J, and K. Friend node O has a relationship with LPN L and M. Therefore, messages addressed to I, J, or K will be stored and forwarded by Friend P, while messages for L or M will be handled by Friend O. This forwarding occurs only when the LPN polls the Friend node for pending messages.
Friend Node Parameters
The LPN must find a “Friend†node and establish a Friendship relationship with it. This process is known as Friend Establishment. We’ll go into more detail later, but first, let’s look at some key parameters that define LPN behavior, as they are set during the Friend establishment process.
1. Â Â Â Â ReceiveDelay is the time between when the LPN sends a request to the Friend node and when it starts listening for a response. This gives the Friend node time to prepare and send back the response.
2. Â Â Â Â ReceiveWindow is the amount of time the LPN spends listening for a response. Figure 2 illustrates the timing of ReceiveDelay and ReceiveWindow.
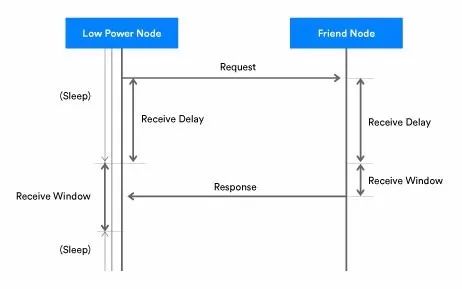
Figure 2 - Timing of ReceiveDelay and ReceiveWindow
3.     PollTimeout defines the maximum time allowed between two consecutive requests from the LPN to its Friend node. If the Friend node doesn’t receive a request before PollTimeout expires, the Friendship will be terminated.
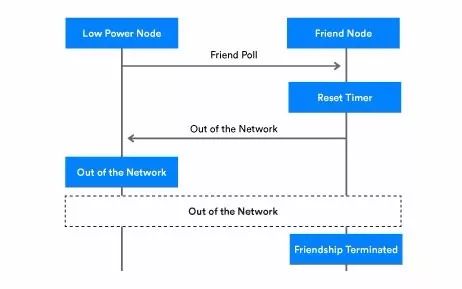
Figure 3 - PollTimeout Timing
Establishing a Friendship
Building a friendship requires several steps, not just a single glance. To establish a Friendship in a Bluetooth mesh network, the following steps are needed:
1.     The LPN sends a Friend Request message. This message isn’t relayed, so only the Friend node within direct range can handle it. Nodes without the Friend feature discard it. The Friend Request includes the LPN’s ReceiveDelay, ReceiveWindow, and PollTimeout parameters.
2. Â Â Â Â Each Friend node in the vicinity of the request can respond with a Friend Offer message, providing details like supported ReceiveWindow size, available message queue size, and RSSI value measured by the Friend node.
3. Â Â Â Â Upon receiving the Friend Offer, the LPN uses an application-specific algorithm to select the best Friend node. Factors like ReceiveWindow size or RSSI values may influence the choice.
4. Â Â Â Â After selecting a Friend node, the LPN sends a Friend Poll message to it.
5. Â Â Â Â The Friend node replies with a Friend Update message, ending the setup process and providing security parameters. At this point, the Friendship is established.
Friend Node Information
Once a Friendship is established, the Friend node stores all messages addressed to the LPN in the Friend Queue. These are known as stored messages. Figure 4 below shows the message exchange between the Friend node and the LPN.
·       When the Friend node receives a message addressed to the LPN, it buffers the message in a storage area called the Friend Queue. In Figure 4, messages 1 and 2 represent LPNs stored in the Friend node.
·       Periodically, the LPN polls the Friend node for any buffered messages.
·       The Friend node replies with the stored message in response to the Friend Poll.
·       After each message is received, the LPN continues polling until it gets a Friend Update message with the MD field set to 0, indicating no more messages are buffered. At this point, the LPN stops polling the Friend node.
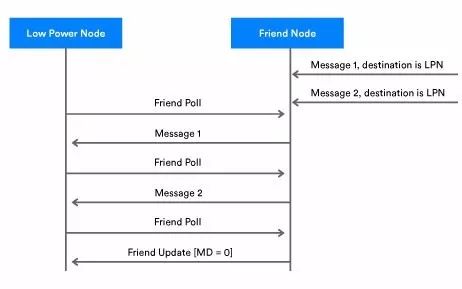
Figure 4 - Friendship Messaging
Security
Security is essential in Bluetooth networks, and this applies to Friendship as well. It uses two special security credentials:
·       Master Security Material : Derived from NetKey or used by other nodes in the same network. Messages encrypted with Master Security Material can be decrypted by any node in the network.
·       Friend Security Material : Also derived from NetKey, but includes additional counter numbers generated by both the LPN and Friend nodes. Messages encrypted with Friend Security Material can only be decrypted by the LPN and Friend that own it.
Which security materials do LPN and Friend nodes use? Here’s a summary:
Messages encrypted with Friend Security Material include:
·        Friend Poll
·        Friend Update
·        Friend Subscription List Add/Remove/Confirm
·        Stored messages passed from the Friend to the LPN
Messages encrypted with Master Security Material include:
·        Friend Clear
·        Friend Clear Confirmation
Depending on the application, messages sent from the LPN to the Friend node may be encrypted using either the Master or Friend security profile.
Termination of Friendships
Friendship can be terminated in certain cases:
·       If the Friend node receives a Friend Subscription List Add/Remove message before the PollTimeout timer expires, the Friendship terminates.
·       The LPN can initiate termination by sending a Friend Clear message to the Friend node, causing the Friendship to end.
Platform Selection Advice
When choosing a platform to implement Friend and LPN features, developers should consider the following guidelines:
·       RAM Capacity: The amount of RAM available determines how many LPNs a Friend node can support and how many messages it can buffer for each LPN.
·       LPN Performance: The power efficiency of selected MCUs and modules is crucial for LPNs. Additionally, the wake-up/warm-up time from sleep to active mode affects the LPN’s responsiveness and delay.
As a developer, I believe we can share your expectations for the Bluetooth Mesh SDK. Then we can explore the "Friendship" concept together!
phone Charging cable,Usb Phone Data Cable Android,iphone charge data cable,Phone data cable adapter
DongGuan BoFan Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.ufriendcc.com
