LED lighting and backlight technology have made remarkable progress in the past decade. As a new generation of green light source, LED light source has appeared in the field of traditional lighting, but there are still many unresolved problems in LED light source.
These include poor consistency, high cost, and poor reliability. The most important issues are stability and reliability issues. Although the life of LED light sources is currently predicted to exceed 50,000 hours. But this life refers to the theoretical life, the life of the light source at 25 ° C. In the actual use process, it will encounter harsh environments such as high temperature and high humidity, amplify LED light source defects, accelerate material aging, and make LED light source fail quickly.

Physical mechanism of failure mode
The LED lamp bead is a system consisting of multiple modules. Failure of each component will cause the LED bead to fail. From the light-emitting chip to the LED lamp bead, there are nearly 30 failure modes, as shown in Table 1, the failure mode table of the LED lamp bead. Here, the LED is divided into two parts, a chip and an external package. Then, the mode and physical mechanism of LED failure are also divided into two types: chip failure and package failure.
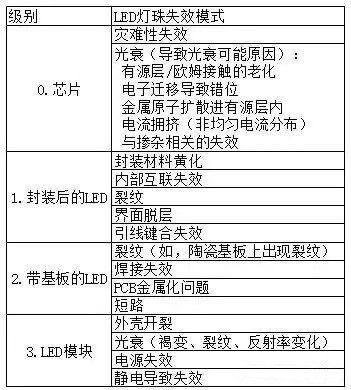
Table 1 LED lamp failure mode
The main factors causing LED chip failure include: static electricity, current and temperature.

Electrostatic discharge can release instantaneous ultra-high voltage, which brings great harm to LED chips. LED chip failure caused by ESD is divided into soft failure and hard failure. The high voltage/current caused by static electricity causes the LED chip to be short-circuited into a hard failure mode. The reason for the short circuit of the LED chip is that the excessive voltage causes the electrolyte to rupture, or the excessive current density is the current path generated in the chip.
A slightly lower voltage/current discharge of static electricity can cause soft failure of the LED chip . Soft failure is usually accompanied by a decrease in the chip's reverse leakage current, which may be caused by the high reverse current causing a portion of the leakage current path to disappear. Compared with vertical LED chips, static electricity is more harmful to horizontal LED chips. Because the electrodes of the horizontal LED chip are on the same side of the chip, the instantaneous high voltage generated by the static electricity is more likely to short the electrodes on the chip, thereby causing the LED chip to fail.
Large currents can also cause LED chip failure: on the one hand, high current will bring higher junction temperature; on the other hand, electrons with high kinetic energy enter the PN junction, which will break Mg-H bond and Ga-N bond. .
The cleavage of the Mg-H bond further activates the carriers of the p-layer, causing the LED chip to have an optical power rise phase at the beginning of aging, and the break of the Ga-N bond forms a nitrogen vacancy. Nitrogen vacancies increase the likelihood of non-radiative recombination, which explains the attenuation of the optical power of the device. The formation of nitrogen vacancies is a very long process to achieve equilibrium, which is the main reason for the slow aging of LED chips.
At the same time, a large current will cause current crowding inside the LED chip, and the density of defects in the LED chip is larger, and the phenomenon of current crowding is more serious. Excessive current density can cause electromigration of the metal, causing the LED chip to fail. In addition, the InGaN LED has a very unstable Mg-H2 complex in the effectively doped p layer under the action of both current and temperature.
The effect of temperature on the LED chip is mainly to reduce the internal quantum efficiency and shorten the life of the LED chip. This is because the internal quantum efficiency is a function of temperature. The higher the temperature, the lower the quantum efficiency. At the same time, the aging effect of the temperature on the material deteriorates the performance of the ohmic contact and the material inside the LED chip. In addition, the high junction temperature causes uneven temperature distribution within the chip, causing strain, thereby reducing internal quantum efficiency and chip reliability. The thermal stress is so large that it may cause the LED chip to rupture.

The main factors causing LED package failure are: temperature, humidity and voltage.
At present, the most in-depth and extensive research is the effect of temperature on the reliability of LED packages. The reason why the temperature causes the LED module and system to fail is as follows:
(1) The high temperature will accelerate the degradation of the packaging material and reduce the performance;
(2) The junction temperature has a great influence on the performance of the LED. Too high a junction temperature will cause the phosphor layer to blacken and carbonize, resulting in a drastic reduction in LED efficacy or catastrophic failure. In addition, since the refractive index and the coefficient of thermal expansion between the silica gel and the phosphor particles do not match, an excessively high temperature causes a decrease in the conversion efficiency of the phosphor, and the higher the proportion of the phosphor blended, the more the light effect decreases.
(3) Due to the mismatch of thermal conductivity between the encapsulating materials, uneven temperature gradient and temperature distribution, cracks may occur inside the material or delamination may occur at the interface between the materials. These cracks and delaminations will cause a decrease in light efficiency. The delamination between the chip and the phosphor layer can reduce the light extraction efficiency. The delamination between the phosphor layer and the potting silica gel can reduce the light extraction efficiency by more than 20%. . The delamination between the silica gel and the substrate may even cause the gold wire to break, causing catastrophic failure.
Through experiments on high-humidity environments, it has been found that the intrusion of moisture not only causes the LED efficacy to decrease, but also may lead to catastrophic failure of the LED. Accelerated experimental research by high temperature and high humidity reliability of 85 °C / 85% RH found that moisture plays an important role in the formation of delamination defects. The delamination phenomenon causes the light effect of LED to decrease, and the surface roughness of different chips is different. Different failure modes.
Storage Battery,Colloid Battery,Lead-Acid Battery,Lead Carbon Battery
Fuzhou Mei Li Cheng Imp&Exp Co., Ltd , https://www.mlc-solar.com
